1.1 Mechanics Explains and predicts physical phenomenon through the study of rigid, deformable, or fluid objects under the action of forces.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 The mechanics of rigid bodies is subdivided into:
The mechanics of rigid bodies is subdivided into:Statics:
.
Dynamics:

~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Mechanics of Materials, because no material is perfectly rigid...
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Incompressible fluids
- liquids:
Compressible fluids
- gas
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
In summary...


What
Can You Do with Statics Knowledge?

Calculate the force in each member of
this structure (a truss) in order to design it to withstand the loads that it
will experience.

Determine the forces that this prosthetic arm will need to withstand to
make exercise possible for the wearer.

Design the joints and support of the Shuttle Remote Manipulator System (SRMS) so that it can be used to pick up and support various payloads.
1.2 Fundamental Concepts and Principles
Aristotle (384-322)
Father of logic and deductive reasoning.
"In all things of nature there is something of the marvelous."
Archimedes (287-212)
greatest mathematician of antiquity
"Eureka! - I have found it!"
Center of mass, boyancy
Newton (1642-1727)"
For every action, there is an equal (in size) and opposite (in direction) reaction force.




Example:
What is the gravitational acceleration on Mars?







a.jpg)


















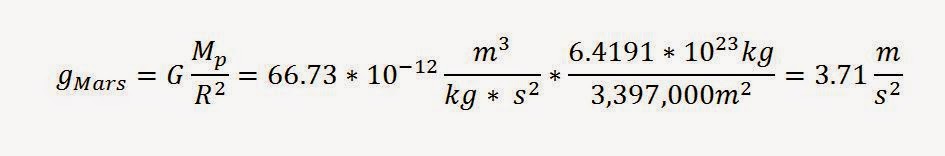








No comments:
Post a Comment